Geo-Targeting Goodness: The Synergy Between GIS and Corporate Social Responsibility
CSR: Corporate Social Responsibility refers to the practices and policies undertaken by organisations to have a positive impact on the world. This can include efforts to improve environmental sustainability, support local communities, ensure fair labor practices, and engage in ethical governance. CSR is no longer just a public relations tool but a core business strategy that drives long-term success.
In today’s interconnected world, the intersection of technology and corporate social responsibility is becoming increasingly vital. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and TechCSR are two powerful tools that, when combined, can create significant positive impacts for businesses, communities, and the environment. This offers companies a strategic advantage in their CSR initiatives, allowing them to target their efforts more effectively, allocate resources efficiently, and ultimately, drive sustainable development.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is no longer a mere checkbox; it’s a strategic imperative. It’s about creating a positive impact on society, the environment, and the economy. But how can organizations ensure their efforts are truly making a difference? The answer lies in precision, and that’s where Geographic Information Systems (GIS) come in.
GIS: The GPS for CSR
GIS technology is a system designed to capture, store, manipulate, analyze, manage, and present spatial or geographic data. It enables organizations to visualize, question, interpret, and understand data in ways that reveal relationships, patterns, and trends. By using GIS, companies can gain insights into a variety of factors such as population demographics, environmental risks, resource availability, and infrastructure development.
Imagine having a bird’s-eye view of your CSR initiatives. With GIS, this vision becomes reality. This powerful tool transforms raw data into actionable insights, helping organizations:
- Pinpoint Impact Areas: Identify communities with the greatest need by overlaying demographic, economic, and environmental data.
- Optimize Resource Allocation: Distribute resources efficiently based on geographic factors, maximizing the impact of every dollar spent.
- Track Progress in Real-Time: Monitor project implementation and measure outcomes with precision.
- Tell Your Story Visually: Create compelling maps and reports to showcase your CSR achievements.
CSR Software: Your Digital Ally
To harness the full potential of GIS for CSR, organizations need robust software solutions. CSR management software, integrated with GIS capabilities, becomes a game-changer. These platforms offer a centralized hub for:
- Project Planning and Management: Set goals, allocate resources, and track progress efficiently.
- Data Collection and Analysis: Gather and analyze data to inform decision-making.
- Reporting and Stakeholder Engagement: Create impactful reports and share your CSR story with stakeholders.
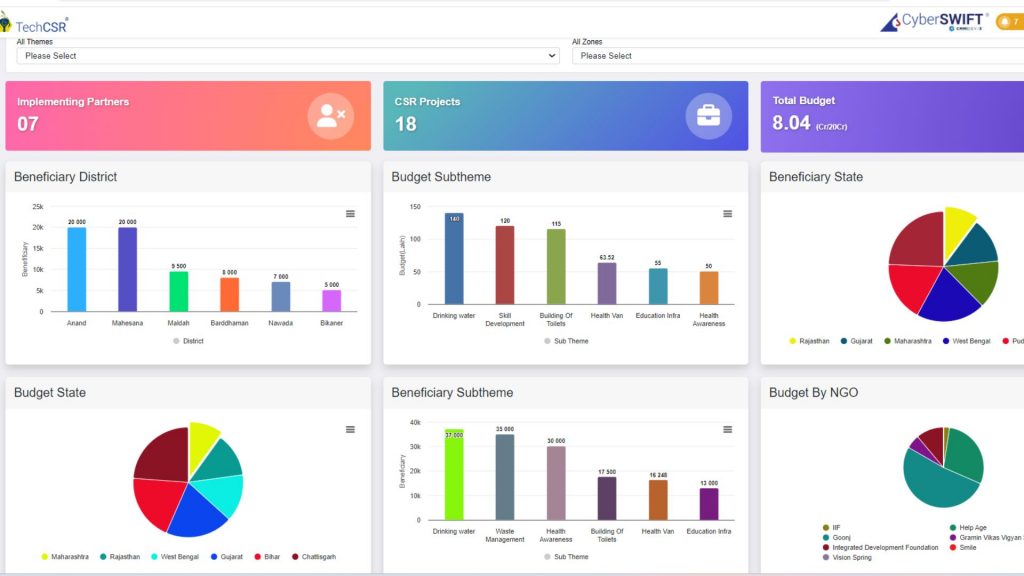
The Future of CSR: Geo-Targeted and Data-Driven
The convergence of GIS and CSR software is ushering in a new era of data-driven, impactful CSR initiatives. The integration of GIS into CSR strategies enables companies to tailor their initiatives to the specific needs of the communities they serve. Here’s how GIS can enhance CSR efforts:
Precision in Community Engagement: By using GIS, companies can identify the exact locations where their CSR activities would be most impactful. For example, a company looking to improve education in underprivileged areas can use GIS to pinpoint schools in need of resources, track progress over time, and ensure that their efforts are making a real difference.
Environmental Stewardship: GIS can help companies monitor and mitigate their environmental impact. For instance, businesses can use GIS to track deforestation rates, manage water resources, or monitor air quality. This data-driven approach allows for more targeted environmental CSR initiatives, such as reforestation projects or pollution reduction programs, ensuring that efforts are concentrated where they are most needed.
Disaster Response and Recovery: In times of crisis, GIS can play a critical role in disaster response and recovery efforts. Companies can use GIS to map out affected areas, coordinate relief efforts, and allocate resources effectively. This ensures that aid reaches those who need it most and that recovery efforts are efficient and effective.
Supply Chain Transparency: GIS can provide insights into the geographic distribution of a company’s supply chain, highlighting areas where ethical concerns might arise, such as labor practices or environmental impact. By addressing these issues proactively, companies can enhance their CSR credentials and build trust with consumers.
Stakeholder Engagement and Reporting: GIS enhances transparency and communication with stakeholders. Interactive maps and data visualizations can be used to report on CSR activities, making it easier for stakeholders to see the impact of a company’s efforts. This not only builds trust but also encourages continued support from investors, customers, and communities.
In conclusion, by leveraging the power of spatial analysis, companies can enhance the effectiveness of their CSR initiatives, leading to greater social, environmental, and economic benefits. As businesses continue to recognize the importance of CSR in their operations, the role of GIS will only become more significant, paving the way for more targeted, impactful, and sustainable corporate practices.


A seasoned professional and dedicated customer advocate, he is an IIM graduate with extensive experience across information technology, the social sector, and consulting. Throughout his career, he has partnered with numerous prominent large enterprises and is currently focused on the business aspects of TechCSR. His expertise spans strategic planning, data analysis, stakeholder engagement, sales strategy, and negotiation. Outside of work, he enjoys unwinding at scenic hill stations.