Here's a quick look at the hierarchy of the Public Healthcare Referral System:
- Medical College & Hospital - These are usually funded and controlled by the state governments and function as medical schools as well as hospitals.
- District & Subdivisional Hospital - The district hospitals are usually controlled by the state governments and serve separate districts and sub-divisions respectively. They are headed by a superintendents
who report to a Chief Medical Officer of Health (CMOH) of respective districts.
- State General Hospital - These are controlled by the respective state governments.
- Rural Hospitals & Block Primary Health Centre - These healthcare centres cater to the medical requirements of the people at the block level in a rural region. Sometimes these function as rural hospitals.
- Primary Health Centre - A Primary Health Centre is a basic rural healthcare facility. It is a single-physician clinic that is equipped with the infrastructure required for minor surgeries.
- Community Health Centre - It acts as a referral centre for patients who require specialized healthcare services. It is usually staffed by general practitioners who provide healthcare to the people in the
area.
- Subcentre - The sub centre is at the periphery of the public healthcare system in rural India. It serves as the contact point for the community to access modern health care. A sub centre is usually equipped
to provide basic medical services including immunization, health education, medicines for minor ailments etc.
 Disease Outbreak Mapping
Disease Outbreak Mapping
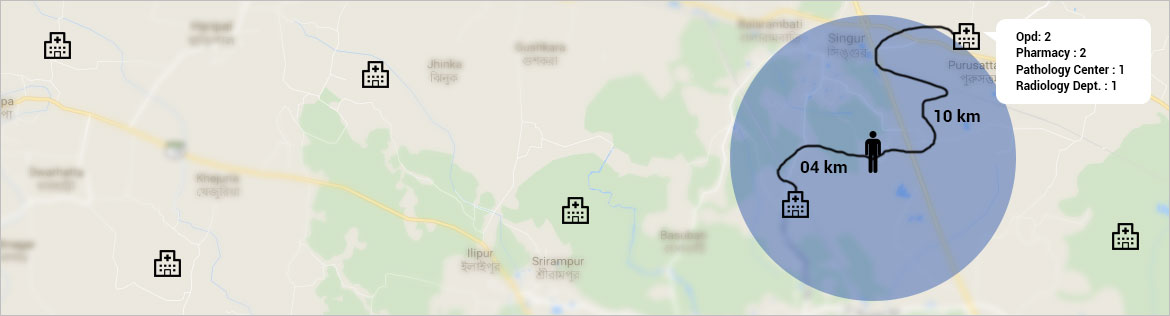
In addition, there are hospitals under local bodies, government of India, non-governmental organizations, privately-owned hospitals and various departments of state government apart from health and family welfare. Mapping these healthcare
centres helps authorities ensure that every individual receives the best possible medical care closest to their homes.
 Disease Outbreak Mapping
Disease Outbreak Mapping